The Drake Passage, located between the southernmost extrimity of South America’s Cape Horn and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica, is a astounding and distinctive location where deep-sea creatures have been perceived to put forward to the surface. This narrow waterway, which connects the Atlantic, Pacific, and Southern Oceans, creates a complex and dynamic ecosystem that supports an astonishingly wide variety of marine life. The Drake Passage is classified by a quirky amalgamation of ocean currents, temperature gradients, and nourishing waters, which together generate an best possible environment for a vast assortment of marine species to propagate.
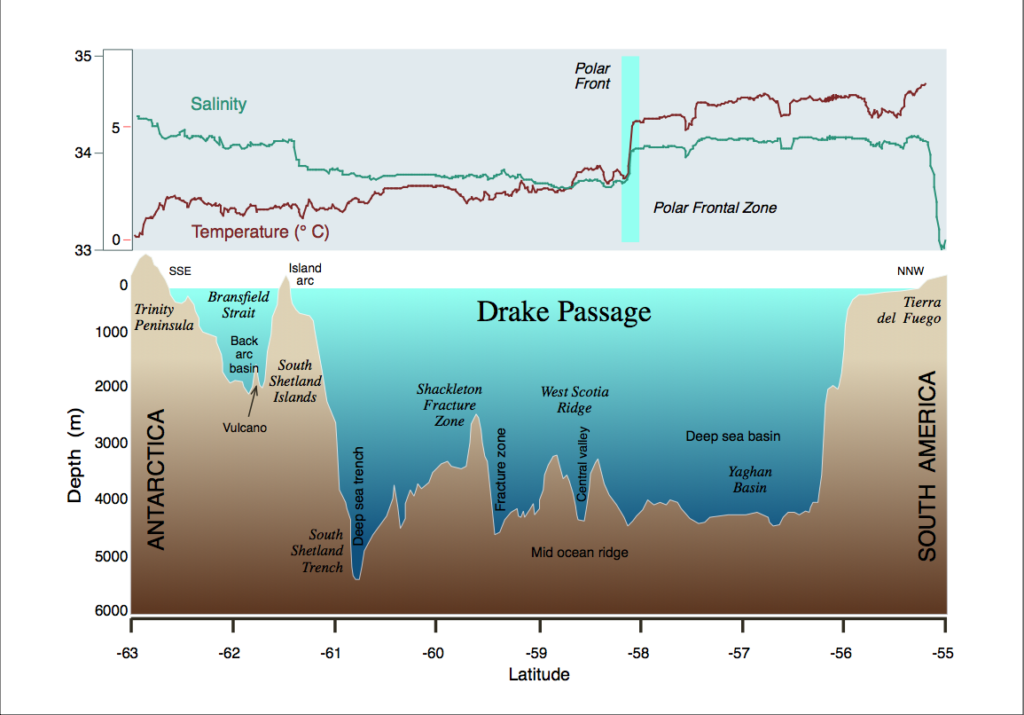
One potential cause for deep-sea creatures coming to the top in this area is the change in ocean currents. Shifts in global ocean circulation patterns can bring these creatures to the surface, and the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, which flows through the Drake Passage, plays a significant role in global oceanic circulation and climate regulation. This current is a critical component of the global ocean conveyor belt, and its flow through the Drake Passage helps to drive the upwelling of nutrient-rich waters, which in turn supports the growth of phytoplankton and other marine life. As a result, the Drake Passage is home to an abundance of marine life, including deep-sea creatures that are rarely seen in other parts of the world.
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current is a key factor in the unique ecosystem of the Drake Passage. This current is driven by strong westerly winds that blow across the Southern Ocean, and it plays a crucial role in the global oceanic circulation of heat, nutrients, and marine life. The current’s flow through the Drake Passage is particularly significant, as it creates a complex and dynamic environment that supports a wide range of marine species. The current’s impact on the global climate is also noteworthy, as it helps to regulate the exchange of heat and nutrients between the Atlantic, Pacific, and Southern Oceans.
In addition to the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, other factors contribute to the unique ecosystem of the Drake Passage. The passage’s location near the Antarctic Convergence, where cold Antarctic waters meet warmer sub-Antarctic waters, creates a unique mixture of species from different oceanic regions. The resulting ecosystem is characterized by an incredible diversity of marine life, including deep-sea creatures that are found nowhere else in the world. The Drake Passage is also home to an array of seabirds, including albatrosses, petrels, and penguins, which feed on the abundant marine life in the area.
The complex interplay of ocean currents, temperature gradients, and nutrient-rich waters in the Drake Passage creates an ideal environment for deep-sea creatures to thrive. The area’s unique ecosystem supports an incredible diversity of marine life, and scientists continue to discover new species and learn more about the complex relationships between the different species that inhabit this remarkable region. As research continues, the Drake Passage remains an fascinating and largely unexplored region of the world’s oceans, with much still to be learned about its unique ecosystem and the deep-sea creatures that call it home.
Another significant reason for deep-sea creatures venturing to the surface is the availability of food. The Drake Passage, situated between South America’s Cape Horn and Antarctica’s South Shetland Islands, is a hotspot for marine life, with an array of wildlife calling this region home. Whales, dolphins, and seabirds are among the many species that feed on the rich marine life in the area, creating a complex food web that supports a diverse range of species. The abundance of food sources near the surface can attract deep-sea creatures, causing them to migrate upwards in search of sustenance.
The Drake Passage is characterized by an upwelling of nutrient-rich waters, which supports the growth of phytoplankton and other marine life. This unique ecosystem creates a rich and diverse food web, with many species relying on the abundant food sources available in the area. Deep-sea creatures, which typically inhabit the dark, food-scarce environments of the deep ocean, may be drawn to the surface by the availability of food in the Drake Passage. This migration can be a vital survival strategy for these creatures, allowing them to take advantage of the abundant food sources and sustain themselves in a challenging environment.
Climate change may also be a factor in deep-sea creatures surfacing. Rising ocean temperatures and acidification can force these creatures to adapt and migrate to new habitats, potentially bringing them to the surface. As the ocean warms and becomes more acidic, deep-sea creatures may find it increasingly difficult to survive in their traditional habitats. In response, they may migrate to new areas in search of more favorable conditions, potentially bringing them to the surface. This migration can be a complex and challenging process, requiring deep-sea creatures to adapt to new environments and find new sources of food.
The impact of climate change on deep-sea creatures is a complex and multifaceted issue. Rising ocean temperatures can alter the distribution and abundance of food sources, making it more difficult for deep-sea creatures to survive. Ocean acidification can also have a profound impact on deep-sea creatures, particularly those with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons. As the ocean becomes more acidic, these creatures may find it increasingly difficult to build and maintain their shells and skeletons, potentially leading to reduced growth rates and increased mortality.
In the Drake Passage, the impact of climate change on deep-sea creatures is likely to be significant. The region’s unique ecosystem, characterized by an upwelling of nutrient-rich waters and a diverse range of marine life, may be particularly vulnerable to changes in ocean temperature and chemistry. As the ocean warms and becomes more acidic, deep-sea creatures in the Drake Passage may be forced to adapt and migrate to new habitats, potentially bringing them to the surface. This migration can have significant implications for the ecosystem as a whole, potentially leading to changes in the distribution and abundance of species and altering the complex food web that exists in the region.
The term “Leviathan” has long been associated with large, mysterious sea creatures that captivate the imagination of scientists and the general public alike. While there is no direct connection between the Drake Passage and the Leviathan mystery, this unique and fascinating region is home to an incredible array of marine life that makes it an attractive area of study for researchers. The Drake Passage, situated between South America’s Cape Horn and Antarctica’s South Shetland Islands, is a complex and dynamic ecosystem that supports a diverse range of species, from massive whales and dolphins to seabirds and giant petrels.
One of the most notable features of the Drake Passage is its incredible array of whale and dolphin species. Humpback whales, with their distinctive songs and acrobatic displays, are a common sight in these waters, as are hourglass dolphins, which are known for their striking color patterns and social behavior. These marine mammals thrive in the nutrient-rich waters of the Drake Passage, where they feed on a variety of fish, krill, and other prey.
In addition to its impressive array of whales and dolphins, the Drake Passage is also home to a diverse range of seabirds. Albatrosses, petrels, and penguins are among the many bird species that call this region home, with some species migrating thousands of miles each year to breed and feed in these waters. Giant petrels, including southern giant petrels and northern giant petrels, are two of the most iconic bird species found in the Drake Passage. These large, powerful birds are known for their distinctive calls and impressive wingspans, and are a common sight in these waters.
The Drake Passage is also characterized by an incredible array of other marine life, including seals, sea lions, and a variety of fish species. The unique combination of cold Antarctic waters and warmer sub-Antarctic waters creates a complex and dynamic ecosystem that supports a diverse range of species. Scientists and researchers are drawn to this region because of its unique environment and diverse marine life, which provide a fascinating opportunity to study the complex interactions between species and their environment.
Despite the many advances that have been made in our understanding of the Drake Passage and its marine life, there is still much to be learned about this fascinating region. Scientists and researchers continue to conduct research in these waters, using a variety of techniques, including satellite tracking, acoustic monitoring, and direct observation. The insights gained from this research have the potential to inform conservation efforts and management practices, helping to protect the unique and diverse marine life of the Drake Passage for future generations.
The intricate and dynamic interplay of ocean currents, climate, and marine life in the Drake Passage gives rise to a captivating environment that continues to fascinate scientists and researchers. This unique region, situated between South America’s Cape Horn and Antarctica’s South Shetland Islands, is characterized by a complex array of ocean currents, temperature gradients, and nutrient-rich waters that support an incredible diversity of marine life. As a result, the Drake Passage has become an ideal location for scientists to study the behavior and habits of deep-sea creatures, and to gain a deeper understanding of the complex ecosystems that exist in our oceans.
The Drake Passage is a natural laboratory for scientists, offering a unique opportunity to study the complex interactions between ocean currents, climate, and marine life. By exploring this region, researchers can gain valuable insights into the natural world and the impact of human activities on the environment. The area’s unique conditions, including its proximity to the Antarctic Circumpolar Current and the upwelling of nutrient-rich waters, create an ideal environment for studying the behavior and habits of deep-sea creatures.
One of the key areas of focus for scientists studying the Drake Passage is the behavior and ecology of deep-sea creatures. By using advanced technologies such as submersibles, remote-operated vehicles (ROVs), and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), researchers can explore the deep-sea environment and gain a better understanding of the complex ecosystems that exist in this region. This research has the potential to inform conservation efforts and management practices, helping to protect the unique and diverse marine life of the Drake Passage for future generations.
In addition to its scientific significance, the Drake Passage is also an important region for understanding the impact of climate change on marine ecosystems. As the ocean warms and becomes more acidic, the delicate balance of the ecosystem in the Drake Passage may be disrupted, potentially leading to changes in the distribution and abundance of species. By studying this region, scientists can gain valuable insights into the potential impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems and develop strategies for mitigating these effects.
The study of the Drake Passage and its inhabitants is a complex and multidisciplinary endeavor, requiring the collaboration of scientists from a variety of fields, including oceanography, marine biology, ecology, and conservation biology. By working together, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the complex ecosystems that exist in this region and develop effective strategies for managing and conserving these ecosystems. As our understanding of the Drake Passage and its inhabitants continues to grow, we are reminded of the importance of protecting this unique and fascinating region for future generations.
Pingback: Rising sea levels due to global warming are a warning sign of a devastating natural disaster